Understanding the human body is essential for comprehending how we function, how to maintain health, and how to address medical issues effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into various Body Parts Name, specifically focusing on the woman body parts, and explore both external and internal body parts. This detailed exploration will provide a holistic understanding of our anatomy.
External Body Parts
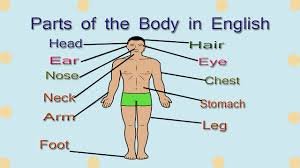
Head and Neck
The head houses critical sensory organs and the brain, which is the control center of the body. Key components include:
- Scalp: Protects the skull and brain.
- Eyes: Visual organs that detect light and send signals to the brain.
- Ears: Organs for hearing and balance.
- Nose: Organ for smell and respiration.
- Mouth: Entry point for food and air; includes the lips, tongue, teeth, and palate.
- Neck: Connects the head to the torso and contains vital structures like the trachea, esophagus, and major blood vessels.
Upper Limbs
The upper limbs are crucial for manipulation and interaction with our environment. They include:
- Shoulders: Provide a wide range of motion for the arms.
- Arms: Include the upper arm, elbow, forearm, wrist, and hand.
- Hands: Consist of the palm, fingers, and thumb, allowing for precise movements and dexterity.
Torso
The torso is the central part of the body, containing many vital organs. Main areas include:
- Chest: Houses the heart and lungs.
- Abdomen: Contains digestive organs like the stomach, liver, intestines, and kidneys.
- Pelvis: Supports the lower limbs and contains reproductive organs.
Lower Limbs
The lower limbs are essential for mobility and support. They consist of:
- Hips: Connect the pelvis to the legs.
- Legs: Include the thigh, knee, calf, and ankle.
- Feet: Comprise the heel, arch, sole, and toes, providing balance and propulsion.
Woman Body Parts
Breasts
Breasts are prominent in women and play a role in lactation. They consist of:
- Mammary glands: Produce milk.
- Areola and nipple: Central area through which milk is expelled.
Reproductive System
The female reproductive system is complex and involves:
- Ovaries: Produce eggs and hormones.
- Fallopian tubes: Transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus.
- Uterus: Nurtures the developing fetus.
- Vagina: Birth canal and the conduit for menstrual flow.
- Vulva: External genital organs including the labia, clitoris, and vestibule.
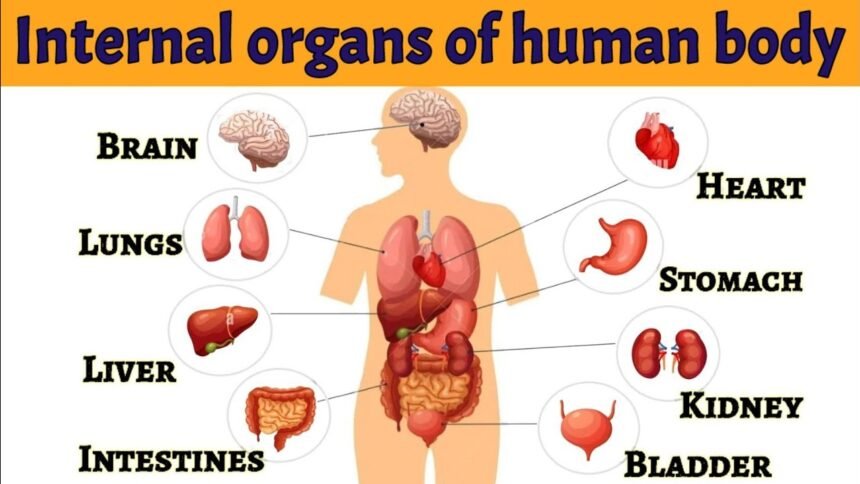
Internal Body Parts
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system controls most functions of the body and mind. Key components are:
- Brain: Main control center for body functions and cognitive processes.
- Spinal cord: Transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
Cardiovascular System
This system circulates blood and includes:
- Heart: Pumps blood throughout the body.
- Blood vessels: Arteries, veins, and capillaries that transport blood.
Respiratory System
The respiratory system is responsible for gas exchange. Main parts are:
- Lungs: Primary organs of respiration.
- Trachea: Windpipe that connects the throat to the lungs.
- Bronchi: Air passages within the lungs.
Digestive System
The digestive system processes food and absorbs nutrients. Key organs include:
- Mouth: Begins the digestive process.
- Esophagus: Transports food to the stomach.
- Stomach: Breaks down food with acids and enzymes.
- Intestines: Absorb nutrients and expel waste.
- Liver: Produces bile and processes nutrients.
- Pancreas: Produces digestive enzymes and hormones.
Urinary System
The urinary system removes waste from the blood and controls water balance. It includes:
- Kidneys: Filter blood to produce urine.
- Ureters: Transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Bladder: Stores urine.
- Urethra: Expels urine from the body.
Endocrine System
The endocrine system regulates bodily functions through hormones. Major glands are:
- Pituitary gland: The “master gland” that controls other endocrine glands.
- Thyroid gland: Regulates metabolism.
- Adrenal glands: Produce hormones like adrenaline and cortisol.
- Pancreas: Regulates blood sugar levels.
- Ovaries/Testes: Produce sex hormones.
Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system supports the immune system. It includes:
- Lymph nodes: Filter lymph fluid and trap pathogens.
- Spleen: Filters blood and supports immune response.
- Thymus: Produces T-cells for the immune system.
- Lymphatic vessels: Transport lymph fluid throughout the body.
Musculoskeletal System
The musculoskeletal system provides structure and movement. Key components are:
- Bones: Provide structure and protect organs.
- Muscles: Enable movement and support.
- Joints: Allow for mobility and flexibility.
- Tendons and ligaments: Connect muscles to bones and stabilize joints.
Integumentary System
The integumentary system protects the body. It includes:
- Skin: The body’s largest organ, providing a barrier against infection.
- Hair and nails: Protect and enhance the skin.
- Sweat and oil glands: Regulate temperature and maintain skin moisture.
50 Important Body Parts Names
- Scalp
- Forehead
- Eyes
- Ears
- Nose
- Mouth
- Lips
- Teeth
- Tongue
- Jaw
- Neck
- Shoulders
- Arms
- Elbows
- Wrists
- Hands
- Fingers
- Chest
- Breasts
- Heart
- Lungs
- Stomach
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Intestines
- Kidneys
- Bladder
- Pelvis
- Hips
- Thighs
- Knees
- Calves
- Ankles
- Feet
- Toes
- Brain
- Spinal cord
- Trachea
- Bronchi
- Esophagus
- Ovaries
- Uterus
- Vagina
- Vulva
- Pituitary gland
- Thyroid gland
- Adrenal glands
- Spleen
- Thymus
- Skin
Understanding these body parts and their functions provides a comprehensive overview of human anatomy. This knowledge is crucial for maintaining health and addressing medical concerns effectively.